Chemical and Biological Fungicides for Preventative Control of Anthracnose
Impact of Chemical and Biological Fungicides for Preventative Control of Anthracnose on an Annual Bluegrass Green (2010), B. B. Clarke, Rutgers University
Abstract
Anthracnose (Colletotrichum cereale) has become a major disease problem on annual bluegrass (Poa annua) putting greens. An integrated and preventative approach remains the most effective management strategy for lessening the severity and incidence of this disease, including the utilization of appropriate cultural practices, and a rotational fungicide program. Low mowing heights, low N or unbalanced fertility, and the onset of specific environmental factors increase the risk for anthracnose development. Previous research has clearly demonstrated the effectiveness and apparent synergy of potassium phosphite (P-K Plus) tank mixed with chlorothalonil (Daconil Ultrex) for reducing anthracnose severity. The objective of this trial was to determine the effectiveness P-K Plus® mixed with different fungicide chemistries, including fludioxonil (Medallion®) and Polyoxin D zinc salt (Endorse®), on anthracnose development and compared to fungicide(s) applied alone. Foliar nitrogen (N) [Gary’s Green Ultra® – 13-2-3 (0.09 lbs N)] and potassium phosphite [P-K Plus – 3-7-18 + 14% potassium phosphite (K2PO3-)] were applied alone or in combination with Medallion® 50 WP (0.33 oz./M) or Endorse® 2.5W (4 oz./M). Foliar N + phosphite treated Poa annua exhibited significantly less anthracnose incidence than the control on both 5-Aug and 19-Aug. Treatments providing the best control were Daconil Ultrex (3.2 oz./M) + Banner MAXX (2 fl. oz./M), and foliar N + phosphite + Medallion (0.33 oz./M), the latter of which provided better anthracnose control (<20% infection) than Medallion (0.33 oz./M) applied alone (Figure 1). Endorse (4 oz./M) applied alone provide better anthracnose control than Medallion (0.33 oz./M) applied alone. As a consequence the foliar N + phosphite did not significantly enhance Endorse efficacy as it did for Medallion (Figure 1). This difference could be due to fungicide mode of action, Medallion working as a contact (similar to chlorothalonil) and Endorse as a systemic. The best turf quality was provided foliar N + phosphite + Medallion (0.33 oz./M) on 5-Aug. due in large part to the added N, which limits anthracnose development (Figure 2). Based on these results and those from 2008 and 2009, utilize a consistent N spoon feeding approach, and apply P-K Plus (potassium phosphite) with either Medallion (0.33 oz. /M) or Daconil Ultrex (7-14 days) to effectively limit anthracnose incidence and severity. Applying this tank mix at shorter intervals will increase disease control. Initiate this program prior to the onset of visual disease symptoms. Rotate fungicide chemistries for added control. Considering annual chlorothalonil and fludioxonil application restrictions and the cost of fungicides, these programs containing P-K Plus should be used as part of an integrated anthracnose management strategy, and to enhance turfgrass color, quality, and vigor.
Daconil Ultrex®, Medallion®, and Banner MAXX® are registered trademarks of Syngenta Professional Products, Endorse® is a registered trademark of Cleary Chemical.
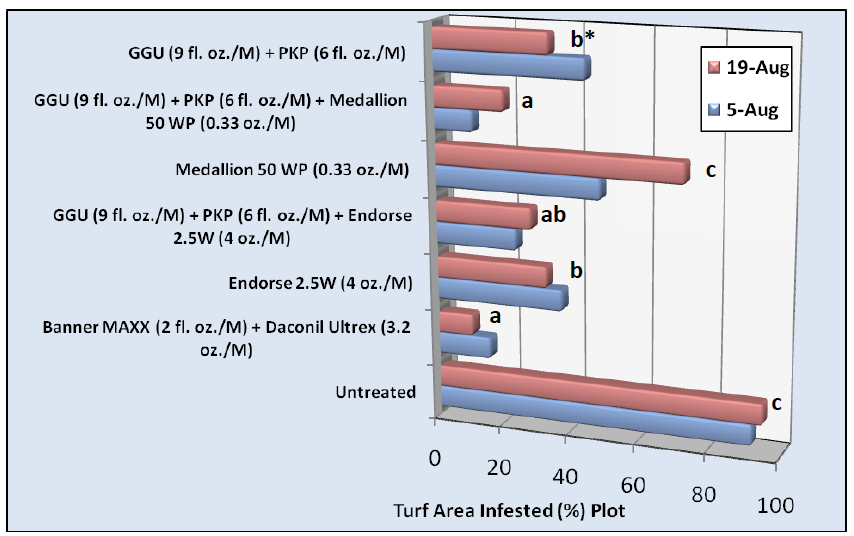
Figure 1. Turf area infested by anthracnose (%) as effected by fungicides, foliar fertilizer program containing potassium phosphite, and combination of a foliar fertilizers and fungicides applied every 14 days.
*Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different using Walker-Duncan k ratio t-test (k=100) and apply only to data from August 19, 2010.
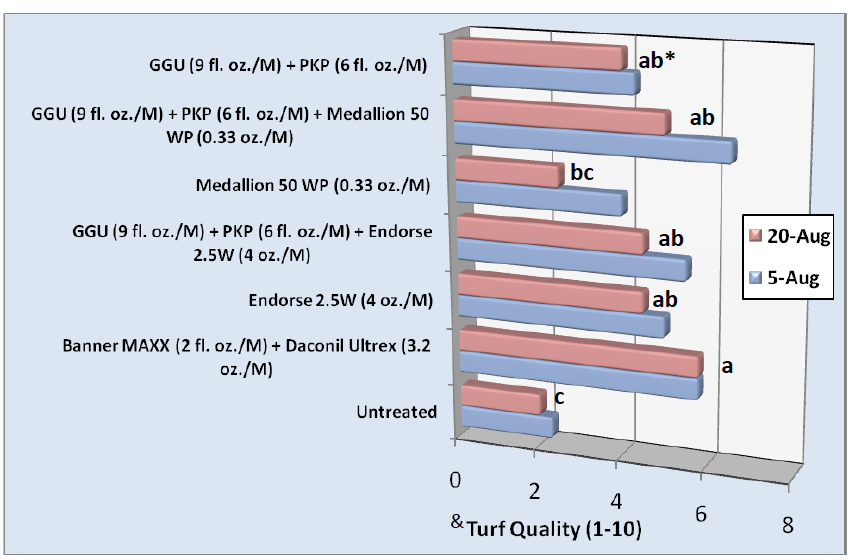
Figure 2. Turf quality as effected by fungicides, foliar fertilizer containing potassium phosphite, and combination of a foliar fertilizer and fungicides applied every 14 days.
*Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different using Walker-Duncan k ratio t-test (k=100) and apply only to data taken from August 20, 2010.
& Turf quality measured as uniformity, color, and disease incidence